- Veronica adamsii
- Veronica agrestis
- Veronica albicans
- Veronica americana
- Veronica amplexicaulis
- Veronica anagallis-aquatica
- Veronica angustissima
- Veronica annulata
- Veronica arganthera
- Veronica armstrongii
- Veronica arvensis
- Veronica barkeri
- Veronica baylyi
- Veronica benthamii
- Veronica biggarii
- Veronica birleyi
- Veronica bishopiana
- Veronica bollonsii
- Veronica brachysiphon
- Veronica breviracemosa
- Veronica buchananii
- Veronica calcicola
- Veronica calycina
- Veronica canterburiensis
- Veronica catarractae
- Veronica catenata
- Veronica chamaedrys
- Veronica chathamica
- Veronica cheesemanii
- Veronica chionohebe
- Veronica ciliolata
- Veronica cockayneana
- Veronica colensoi
- Veronica colostylis
- Veronica corriganii
- Veronica cryptomorpha
- Veronica cupressoides
- Veronica decora
- Veronica decumbens
- Veronica densifolia
- Veronica dieffenbachii
- Veronica dilatata
- Veronica diosmifolia
- Veronica elliptica
- Veronica epacridea
- Veronica evenosa
- Veronica filiformis
- Veronica flavida
- Veronica gibbsii
- Veronica glaucophylla
- Veronica haastii
- Veronica hectorii
- Veronica hederifolia
- Veronica hookeri
- Veronica hookeriana
- Veronica hulkeana
- Veronica insularis
- Veronica javanica
- Veronica jovellanoides
- Veronica kellowiae
- Veronica lanceolata
- Veronica lavaudiana
- Veronica leiophylla
- Veronica ligustrifolia
- Veronica lilliputiana
- Veronica linifolia
- Veronica lyallii
- Veronica lycopodioides
- Veronica maccaskillii
- Veronica macrantha
- Veronica macrocalyx
- Veronica macrocarpa
- Veronica masoniae
- Veronica melanocaulon
- Veronica mooreae
- Veronica murrellii
- Veronica notialis
- Veronica obtusata
- Veronica ochracea
- Veronica odora
- Veronica officinalis
- Veronica pareora
- Veronica parviflora
- Veronica pauciramosa
- Veronica pentasepala
- Veronica perbella
- Veronica peregrina
- Veronica persica
- Veronica petriei
- Veronica phormiiphila
- Veronica pimeleoides
- Veronica pinguifolia
- Veronica planopetiolata
- Veronica plebeia
- Veronica polita
- Veronica poppelwellii
- Veronica propinqua
- Veronica pubescens
- Veronica pulvinaris
- Veronica punicea
- Veronica quadrifaria
- Veronica rakaiensis
- Veronica raoulii
- Veronica rigidula
- Veronica rivalis
- Veronica rupicola
- Veronica salicifolia
- Veronica salicornioides
- Veronica saxicola
- Veronica scopulorum
- Veronica scrupea
- Veronica scutellata
- Veronica senex
- Veronica serpyllifolia
- Veronica simulans
- Veronica societatis
- Veronica spathulata
- Veronica speciosa
- Veronica spectabilis
- Veronica stenophylla
- Veronica stricta
- Veronica strictissima
- Veronica subalpina
- Veronica subfulvida
- Veronica tairawhiti
- Veronica tetragona
- Veronica tetrasticha
- Veronica thomsonii
- Veronica topiaria
- Veronica townsonii
- Veronica traversii
- Veronica treadwellii
- Veronica trifida
- Veronica triphyllos
- Veronica truncatula
- Veronica tumida
- Veronica urvilleana
- Veronica venustula
- Veronica verna
- Veronica vernicosa
- Veronica zygantha
- = Beccabunga Hill, Brit. Herb. 94 (1756)
- = Hebe Comm. ex Juss., Gen. Pl. 105 (1789)
- = Panoxis Raf., Med. Fl. 109 (1830)
- = Pygmea Hook.f., Handb. New Zealand Fl. 217 (1864) nom. illeg., non Pygmaea Stackhouse 1809
- ≡ Chionohebe B.G.Briggs & Ehrend., Contr. Herb. Austral. 25: 1 (1976) nom. nov. pro Pygmea Hook.f. 1864
- = Parahebe W.R.B.Oliv., Rec. Domin. Mus. 1: 229 (1944)
- = Leonohebe Heads, Bot. Soc. Otago Newsl. 5: 4 (1987)
- = Heliohebe Garn.-Jones, New Zealand J. Bot. 31: 323 (1993)
- = Hebejeebie Heads, Bot. Soc. Otago Newsl. 36: 11 (2003)
Annual to perennial herbs, sub-shrubs, and shrubs, rarely small trees; cosexual or gynodioecious, rarely dioecious. Stems prostrate to erect. Leaves opposite and usually decussate, sometimes alternate when subtending flowers, simple, entire, toothed, or crenate, or rarely pinnatifid, linear to broadly obovate to reniform; venation pinnate or sometimes palmate at the base and pinnate above, often obscure. Inflorescence terminal or lateral, bracteate raceme or compound raceme or spike, sometimes flowers solitary in axils of alternate or opposite leaves and these occasionally bibracteate. Calyx lobes 4, or rarely a 5th usually smaller posterior lobe, equal or the posterior pair shorter, shortly united at base or sometimes the anterior pair fused, rarely the posterior pair fused. Corolla tube very short to >> calyx, usually cylindrical or sometimes widening or narrowing towards throat; limb usually zygomorphic, rarely actinomorphic; lobes 4 or 5, usually divided more deeply between the anterior and lateral lobes; nectar spur absent; throat open. Stamens 2, rarely 3, epipetalous on corolla tube, usually exserted, rarely included, sometimes (♀ plants) sterile. Nectarial disc surrounding base or enclosing lower ½ of ovary. Ovary bilocular, rarely trilocular; placenta hemispherical with scattered ovules or peltate with marginal ovules; style short to long; stigma usually exserted, rarely included. Capsule ovoid, conical, obcordate, or didymous; apex acuminate, acute, truncate, emarginate, or deeply notched; locules 2, rarely 3; dehiscence septicidal or loculicidal or both. Seeds 6–c. 100, discoid, elliptic, ovoid, cup-shaped or fusiform, usually smooth to finely colliculate, sometimes ridged or tuberculate, wing usually absent or sometimes narrow.
| 1 | Adult leaves < 5 mm long; low-growing herbs, sub-shrubs, compact cushion shrubs, or whipcord and semi-whipcord shrubs | 2 |
| Adult leaves (including petiole if present) mostly > 5 mm long; herbs, sub-shrubs, shrubs, or trees, but never whipcord or semi-whipcord shrubs and if cushion-forming then leaves lobed to pinnatifid | 22 | |
| 2 | Stems prostrate, leaves orbicular to elliptic; corolla blue or white; nectar guides present | 3 |
| Stems erect, ascending, or cushion- or mat-forming; corolla white (sometimes purplish in V. densifolia); nectar guides absent | 4 | |
| 3 | Short-lived perennial herb; lamina entire, dull grey-green and ciliate; flowers solitary or paired on short peduncles < 10 mm long; corolla blue with flat lateral lobes | lilliputiana |
| Perennial sub-shrub; lamina sometimes entire or usually with 1(–2) pairs of teeth, glossy bright or reddish-green and glabrous; flowers 8–20 in pedunculate racemes 60–250 mm tall; corolla white or pink with folded lateral lobes … | decora | |
| 4 | Alpine cushion plants (sub-shrubs); leaves soft, imbricate; calyx and corolla 5-merous | 5 |
| Montane to alpine wiry (whipcord and semi-whipcord)) sub-shrubs or shrubs; leaves firm and appressed; calyx and corolla 4-merous | 9 | |
| 5 | Mat- or cushion-forming sub-shrubs with decussate, imbricate leaves; leaves widest below middle, concave and often keeled, with thickened, minutely papillate upper margin; leaf hairs usually < 0.4 mm long; corollas > 7 mm diameter; corolla tube shorter than calyx; stamen filaments > 1 mm long | densifolia |
| Cushion plants with sub-decussate imbricate leaves; leaves widest above middle, concave but never keeled, with upper margin smooth and not thickened; leaf hairs usually > 0.4 mm long (up to 1.4 mm); corolla < 7 mm diameter; corolla tube longer than calyx; stamen filaments < 0.8 mm long | 6 | |
| 6 | Inner leaf surfaces with a tight band of densely distributed appressed hairs near the middle of the leaf (rarely reduced to a tight patch of isolated to sparsely distributed appressed hairs); outer leaf surfaces sometimes densely hairy on upper portion; leaf margins sparsely to densely ciliate on the lower ⅔ of the margin and glabrous above except for a tuft of hairs at the apex, or sometimes ciliate for the whole margin | thomsonii |
| Inner leaf surfaces glabrous or with isolated hairs, if sparsely hairy then hairs evenly distributed on upper portion and never arranged in a tight patch or band; outer leaf surfaces variously glabrous or hairy on upper portion but never densely hairy; leaf margins variously glabrous to densely ciliate, with hairs generally on the upper margins only and becoming glabrous below | 7 | |
| 7 | Leaves ciliate with isolated to sparsely distributed hairs and no apical tuft; inner leaf surfaces with isolated to sparsely distributed hairs (generally 6 or more hairs; rarely glabrous in some Mount Arthur and Lead Hills individuals); ovary apex (and often capsule apex) densely hairy | pulvinaris |
| Leaves ciliate with sparsely to densely distributed hairs often with a dense apical tuft; inner leaf surfaces glabrous (rarely with 1–6 isolated hairs); ovary apex and capsule apex glabrous (rarely hairy in some eastern Fiordland individuals) | 8 | |
| 8 | Leaf and bract margins sparsely to densely ciliate; corolla lobes obovate to very broadly obovate; capsules 2.4–3.4 mm long; seeds 0.7–1.1 mm long; alpine herbfield and cushion field, exposed rock outcrops and tors | ciliolata |
| Leaf and bract margins glabrous or with isolated hairs only; corolla lobes narrowly to broadly ovate; capsules 1.8–2.5 mm long; seeds 0.5–0.8 mm long; wet gullies and snow banks | chionohebe | |
| 9 | Inflorescence a terminal spike of sessile opposite bisexual flowers; capsules weakly flattened, truncate or emarginate; leaves mostly bright glossy green (or yellow- to brown-tinted) | 10 |
| Inflorescence a lateral raceme of shortly stalked alternate unisexual flowers; capsules angustiseptate, acute; leaves dull grey-green (glaucescent in V. cupressoides) | 19 | |
| 10 | Groove between connate leaf bases visible, not hidden by leaf below; anterior calyx lobes fused to > ½-way, usually completely (except in V. propinqua, included in this lead, where they may be almost free or fused to ⅓-way) | 11 |
| Groove between connate leaf bases hidden by leaf below, or rarely a very short portion visible; anterior calyx lobes free or fused no more than the basal ⅓ | 16 | |
| 11 | Foliage aromatic, glaucous; calyx bilabiate because both posterior pair and anterior pair fused; corolla lobes pink or mauve, about equal in width; capsule turgid | cupressoides |
| Foliage not aromatic, green or yellowish; posterior calyx lobes always free; anterior fused or free; corolla lobes white, the anterior narrower than the others; capsule latiseptate | 12 | |
| 12 | Anterior calyx lobes free or fused at the base to about ⅓-way; leaf node marked by a distinct but shallow horizontal groove or line | propinqua |
| Anterior calyx lobes fused to > ½-way; leaf node indistinct | 13 | |
| 13 | Leaves thick, keeled; branchlets usually glossy, firm in texture, and ochre-coloured when fresh (north-west Nelson) | ochracea |
| Leaves thin, not keeled; branchlets not glossy, flexible or succulent and green when fresh (Canterbury, Otago) | 14 | |
| 14 | Leaves with a small, blunt mucro, widely spreading when dry and encircling branchlets (Canterbury: Waimakariri and Rangitata catchments) | armstrongii |
| Leaves subacute to rounded, but not mucronate, at apex, spreading slightly when dry | 15 | |
| 15 | Internodes 1.2–3.8 mm long, so that leaves do not overlap, lamina flush with stem, especially when dry, anterior calyx lobes fused ½-way or more (western Marlborough, north Canterbury) | salicornioides |
| Internodes 1.3–1.8 mm long; leaves overlapping at least slightly; anterior calyx lobes generally completely fused (Otago, Southland) | annulata | |
| 16 | Leaf veins close to abaxial surface and prominent, forming parallel longitudinal ribs, especially evident when dry | 17 |
| Leaf veins sunken and obscure even when dry (leaf may be longitudinally wrinkled when dry but lacks discrete ribs) | 18 | |
| 17 | Leaves deltoid, acute to mucronate at apex; corolla tube ≥ calyx | lycopodioides |
| Leaves rounded, obtuse to rounded at apex; corolla tube ≤ calyx | poppelwellii | |
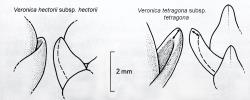
| 18 | Leaf lamina not thickened at apex (South Island) | hectorii |
| Leaf lamina thickened at apex (North Island) | tetragona | |
| 19 | Leaf apex reaching, but not extending beyond, the connate junction of the pair above; back of leaf swollen, rounded | tumida |
| Leaf apex extending beyond the connate junction of the pair above; back of leaf not swollen (although the apex may be), straight from base to apex | 20 | |
| 20 | Leafy branchlets with 4 flat faces, giving square cross-section | quadrifaria |
| Leafy branches with 4 grooved or hollowed faces, to give cruciform cross-section | 21 | |
| 21 | Leaves > 2–6 mm long; apex swollen and rounded with a prominent terminal hydathode | hookeri |
| Leaves 1–2.8 mm long; apex acute, not swollen; hydathode absent | tetrasticha | |
| 22 | Inflorescences terminating growth of vegetative shoot and subsequent new growth (if present) initiating below flowering zone; sometimes the floral bracts are leaf-like but then alternating | 23 |
| Inflorescences strictly lateral racemes or compound racemes with the vegetative growth of the shoot continuing during and after flowering; floral bracts usually much smaller than leaves and more-or-less sharply delineated from them (but note: in V. javanica – included in this lead – the tiny, pale, sessile flowers can appear to be solitary or clustered in leaf axils because the inflorescence doesn’t elongate until fruiting) | 47 | |
| 23 | Flowers sessile or pedicel 1–3(–10) mm long; floral bracts opposite or alternate and at least the upper ones distinctly different from the opposite leaves | 24 |
| Flowers long-pedicellate; floral bracts alternate but otherwise leaflike | 43 | |
| 24 | Stems herbaceous (annual or short-lived perennial weeds); corolla tube short (< 1 mm long); flowers often blue, sometimes white | 25 |
| Stems woody (sub-shrubs to shrubs); corolla tube > 1 mm long; flowers mostly white, sometimes tinged pink or purplish or (only in V. benthamii of Auckland Is., Campbell I.) strongly blue | 29 | |
| 25 | Middle stem leaves and lower bracts divided digitately almost to base | 26 |
| All leaves at most toothed or crenate but not deeply divided | 27 | |
| 26 | Corolla 4–6 mm diameter; capsule 3–5 × 4–6 mm; seeds cup-shaped, dark, wrinkled on outer face, 1.3–1.8 mm long | triphyllos |
| Corolla 1–1.5 mm diameter; capsule 2.5–3.2 × 3.2–4.2 mm; seeds elliptic, flattened, straw-yellow to pale brown, smooth, 0.9–1.2 mm long | verna | |
| 27 | Plants completely glabrous; corolla white without nectar guides | peregrina |
| Plants hairy; corolla pale to bright blue with darker nectar guides (very rarely all white) | 28 | |
| 28 | Stems ascending to erect from single tuft of roots; stem hairs of 2 kinds: (1) dense, bifarious, short, and antrorse, and (2) scattered, uniform, long, and spreading; flowers bright blue (very rarely white) | arvensis |
| Stems rooting at lower nodes; stem hairs all short and uniform; flowers pale blue, fading white | serpyllifolia | |
| 29 | Flowers all opposite | 30 |
| Flowers spiralled (lowest rarely opposite) | 36 | |
| 30 | Leaf margins densely hairy; corolla strongly blue, often 5(–6)-lobed (Auckland & Campbell Is) | benthamii |
| Leaf margins glabrous or with a few short hairs near the base; corolla white or rarely tinged pink or purplish (NI, SI, Auckland & Campbell Is) | 31 | |
| 31 | Leaf margin abruptly narrowed to distinct petiole, making a shield-shaped sinus in the vegetative bud; corolla lobes spreading; anthers exserted | 32 |
| Leaf margin cuneately narrowed to broad connate base, making an acute, narrow sinus in the vegetative bud; corolla lobes recurved; anthers held at corolla throat | 33 | |
| 32 | Leaf margin rounded in section; stomata distinct on both surfaces of lamina; inflorescence of terminal spikes only; bracts ≥ calyx; corolla lobes broadly elliptic to suborbicular; stigma dark magenta (west Nelson & north Westland only) | masoniae |
| Leaf margin sharply bevelled; stomata on abaxial lamina surface only (except on both surfaces at Arthur’s Pass); inflorescences of terminal and lateral spikes; bracts not overtopping calyx; corolla lobes narrowly to broadly elliptic; stigma pale green, white, or brownish (NI, SI, subantarctic Is) | odora | |
| 33 | Inflorescences of compound spikes: dense terminal heads of lateral and terminal sessile spikes | 34 |
| Inflorescences simple spikes (occasionally lateral as well, but if so then shortly pedunculate) | kellowiae | |
| 34 | Leaves bright green, fleshy, usually narrowed into a petiole; calyx lobes usually linear, glabrous or minutely ciliolate, 4.0–8.5 mm long | macrocalyx |
| Leaves dark green, coriaceous or rigid, not or only slightly narrowed to a petiole; calyx lobes elliptic to lanceolate, either minutely ciliolate or ciliate, 3.0–5.5 mm long | 35 | |
| 35 | Leaves coriaceous but not rigid, often shallowly toothed; margin glabrous throughout or minutely ciliolate at base; calyx lobes minutely ciliolate | haastii |
| Leaves rigid, entire; margin ciliate at base; calyx lobes long-ciliate | epacridea | |
| 36 | Flowers in dense simple terminal spikes barely wider than the leafy branchlet; corolla white; anthers magenta or purple; capsules latiseptate | 37 |
| Flowers in diffuse compound spikes or panicles wider than the leafy branchlet; corolla white, pink, or purplish; anthers pale cream or yellowish | 38 | |
| 37 | Bracts 3–5 × 1.7–2 mm, usually all subtending flowers; calyx lobes 4, 2.5–4 mm long, linear to narrowly elliptic; corolla tube 1.5–2 mm long, lobes elliptic to orbicular; anthers exserted, purple | murrellii |
| Bracts 5–7 × 1–1.5 mm, usually numerous sterile ones at base of inflorescence; calyx lobes 4–5, 3.5–6 mm long, linear to narrowly ovate; corolla tube 3–6 mm long, lobes linear to narrowly elliptic, sometimes suborbicular; anthers presented at corolla throat, magenta | petriei | |
| 38 | Leaves narrowly elliptic to oblanceolate or spathulate, < 10 mm wide | 39 |
| Leaves lanceolate, ovate, oblong, elliptic, rhomboid, obovate to orbicular, (5–)10–25(–35) mm wide | 42 | |
| 39 | Leaves oblanceolate to spathulate, widest in distal half; anterior calyx lobes fused nearly to apex (except at Mt Cass, Canterbury) | 40 |
| Leaves narrowly elliptic, widest at about the middle; anterior calyx lobes free | 41 | |
| 40 | Leaves 7–17(–25) mm long; apex subacute to acute, subapiculate; margin serrate with (0–)2–4(–8) pairs of teeth; calyx usually without posterior lobe | raoulii |
| Leaves 4–9(–15) mm long; apex obtuse to rounded; margin entire to crenate, with up to 3 pairs of crenations; calyx with small, posterior 5th lobe | maccaskillii | |
| 41 | Posterior 5th calyx lobe present; corolla (6–)7–8 mm diam | pentasepala |
| Posterior 5th calyx lobe absent; corolla 4–5 mm diam | scrupea | |
| 42 | Inflorescence compact at flowering, with long, glandular hairs; corolla > 10 mm diam.; leaves dull | lavaudiana |
| Inflorescence diffuse at flowering, with short, eglandular or glandular hairs; corolla < 10 mm diam.; leaves glossy | hulkeana | |
| 43 | Lamina circular to reniform, cordate at base, crenate; pedicels 15–40 mm long; corolla 8–10 mm diameter; fruit and seeds absent in New Zealand | filiformis |
| Lamina ovate to broadly ovate, truncate at base, toothed or bluntly lobed; either pedicels > 15 mm long or corolla < 5 mm diameter; capsule angustiseptate; seeds cupped around short funicle, finely papillate | 44 | |
| 44 | Capsule glabrous; pedicel hairs in 1 row; calyx lobes widest at base, with a fringe of long, straight, eglandular cilia on margins; seeds dark, > 2 mm long; leaf lobes in 1–2 pairs with large terminal lobe | hederifolia |
| Capsule hairy on edges or all over; pedicel hairy all around; calyx lobes widest about middle, with short or long eglandular or glandular hairs at the margins; seeds pale to mid-brown, < 2 mm long; leaf teeth in 2–8 pairs, evenly serrate or serrate-crenate | 45 | |
| 45 | Corolla 8–12 mm diameter when fully open; style 1.5–3 mm long; capsule 3.5–4 × 6–7 mm, sinus shallow, lobes spreading and keeled on edges, strongly veined when dry | persica |
| Corolla < 5 mm diameter when fully open; style < 1.5 mm long; capsule < 5 mm at widest point, sinus shallow or deep, lobes erect and rounded to bluntly keeled on edges, not or weakly veined when dry | 46 | |
| 46 | Stem hairs bifarious; pedicel hairs short eglandular and long glandular; calyx lobe margins with long glandular hairs; style < 1 mm long; capsule with rounded lobes, deep sinus, and short, glandular hairs on margin | agrestis |
| Stem hairs uniform; pedicel hairs all short, eglandular; calyx lobe margins with short, eglandular hairs; style 1–1.5 mm long; capsule with rounded lobes, shallow sinus, and dense, short, eglandular hairs all over with short, glandular hairs on margins | polita | |
| 47 | Herbs; flowers blue or sometimes white or pinkish, with very short corolla tube; stamen filaments tapering to very slender and curved base | 48 |
| Shrubs, or low or mat-forming sub-shrubs, or trees with woody stems; flowers usually white or sometimes blue, magenta, or pink with short to long corolla tube; stamen filaments broad or slender at base | 57 | |
| 48 | Plants glabrous or with very few and scattered eglandular or glandular hairs; stems often hollow (wetland plants or in seepages and damp hollows) | 49 |
| Stems and leaves (at least beneath) hairy; stems solid (plants of drier habitats) | 52 | |
| 49 | Stems slender, 1–2 mm thick, straggling; leaves linear to narrow-lanceolate, usually 1–6 mm wide, rarely to 12 mm, with distant, very shallow teeth; inflorescences mostly single at each node; capsule didymous with a deep sinus and 2 rounded flattened lobes; seeds 1.2–1.4 mm long | scutellata |
| Stems stout (usually > 5 mm thick), erect above; leaves narrowly lanceolate to elliptic to ovate, usually > 10 mm wide but sometimes narrower, with fine to coarse close teeth; inflorescences mostly 2 at each node; capsule broadly ovoid to suborbicular, truncate or shallowly emarginate; lobes weakly flattened at base and more strongly towards the apex; seeds 0.5–0.7 mm long | 50 | |
| 50 | Leaves that subtend the inflorescences shortly petiolate and distinctly serrate; pedicels 7–14 mm long; corolla 7–10 mm diameter, tube glabrous inside; style 3.5–4 mm long | americana |
| Leaves that subtend the inflorescences sessile to amplexicaul, finely serrate or more or less entire; pedicels 3–8 mm long; corolla 3.5–7 mm diameter; tube sparsely to densely hairy inside; style 1.5–2.5 mm long | 51 | |
| 51 | Leaves dull pale green; corolla 5–7 mm diameter, with ovate to rhomboid lobes and purple veins on all lobes; bracts < pedicels | anagallis-aquatica |
| Leaves somewhat glossy mid-green; corolla 3–5 mm diameter, with rounded lobes and pink veins on the posterior and lateral lobes only; bracts mostly > pedicels | catenata | |
| 52 | Flowers subsessile on pedicels 0.5–1 mm long; corolla never opening, lobes 1–1.5 mm long, white or pale pink without nectar guides | javanica |
| Flowers subsessile to pedicellate; corolla opening although sometimes closed in dull or cool weather, lobes usually > 2 mm long, rarely 1–1.5 mm long, white, pink, blue, or bluish, with or without nectar guides | 53 | |
| 53 | Hairs of stems, pedicels, and margins of leaves and calyx very short (c. 0.1 mm long), although sparse, longer hairs may be present on leaf and calyx surfaces; leaves deltoid and sharply serrate to biserrate; style 0.8–1.5 mm long | plebeia |
| Hairs of stems and pedicels all > 0.5 mm long; very short hairs (c. 0.1 mm long) absent; leaves ovate to orbicular, sometimes broadly deltoid, usually serrate-crenate; style > 1.8 mm long | 54 | |
| 54 | Leaves about as broad as long, or broader; leaf teeth in 3–6 pairs; flowers (5–)8–30 per inflorescence | 55 |
| Leaves longer than broad; leaf teeth in (4–)6–12 pairs; flowers 2–8 per inflorescence | 56 | |
| 55 | Corolla blue with dark blue nectar guides; inflorescence hairs all eglandular; pedicel hairs in 1 row; capsule ciliate on margins | calycina |
| Corolla white with magenta nectar guides; inflorescence hairs mixed glandular and eglandular; pedicel hairs all around; capsule glabrous | jovellanoides | |
| 56 | Leaf base truncate to cordate; apex obtuse to rounded; leaf margin serrate-crenate; pedicels 5–10 mm long | chamaedrys |
| Leaf base cuneate; apex shortly acuminate; leaf margin finely and shortly dentate; pedicels 1–1.5 mm long | officinalis | |
| 57 | Leaves with a thick, transparent, yellowish cuticle; marginal hairs irregularly branched (low sprawling to sub-erect shrubs confined to alpine habitats in Fiordland) | notialis |
| Leaves with a thin glossy or dull waxy cuticle; marginal hairs simple or absent | 58 | |
| 58 | Apical vegetative buds small, leaves diverging early and while still not fully grown; capsules turgid or angustiseptate, often notched or obtuse; ovules/seeds scattered on surface of placenta or in 2 adjacent rows; herbs, cushion shrubs, low, softly woody sub-shrubs, sometimes small, woody shrubs to 0.5 m tall; leaves often serrate or crenate, sometimes entire | 59 |
| Apical vegetative buds large, formed of several overlapping pairs of leaves that are appressed at their margins until fully grown; capsules latiseptate, often acute; ovules/seeds marginal on flattened placenta; distinctly woody low shrubs to small trees; leaves usually entire or sometimes toothed | 77 | |
| 59 | Leaves all entire | 60 |
| Leaves mostly toothed, crenate or lobed | 63 | |
| 60 | Lamina elliptic to ovate, bronze-green; margin thickened and minutely papillate near apex; flowers sessile; calyx lobes ciliolate near base; corolla 5-lobed | densifolia |
| Lamina narrow-oblong or narrow-elliptic to narrowly lanceolate, bright glossy green above; margin not thicker than rest of lamina, smooth; flowers on a distinct short to long pedicel; calyx glabrous; corolla 4-lobed (or rarely the posterior lobe divided) | 61 | |
| 61 | Low and usually compact mat-forming sub-shrub with trailing stems; leaves narrowly elliptical; peduncle 1–2 mm long | planopetiolata |
| Small, softly woody sub-shrub with trailing to erect stems; leaves linear to narrowly oblong; peduncle > 10 mm long | 62 | |
| 62 | Corolla rotate, tube < 1.5 mm long, shortly hairy inside; nectar guides magenta; stamen filaments > 4–8 mm long; style > 4–9 mm long | linifolia |
| Corolla funnelform, tube 1.2–3.5 mm long, glabrous; nectar guides absent or 2(–4) faint lines on posterior lobe; stamen filaments 1–3 mm long; style 2–4 mm long | colostylis | |
| 63 | Inflorescence with 1–3(–7) flowers; corolla tube (1.5–)2–7 mm long; lateral corolla lobes not longitudinally folded about the anthers; capsule angustiseptate, often (in low-growing alpine plants) hygrochastic | 64 |
| Inflorescence with (4–)7–30 flowers; corolla tube 1–2 mm long; lateral corolla lobes longitudinally folded about the stamens; capsule weakly angustiseptate or turgid, xerochastic | 72 | |
| 64 | Lamina glabrous on surfaces but the margin sometimes sparsely ciliate, especially near the base or ciliolate throughout, bright green or bronze-green | 65 |
| Lamina surface hairy with short or long, glandular or eglandular hairs, dull greyish-green or sometimes brownish | 69 | |
| 65 | Erect or sometimes decumbent to sub-erect shrubs to 0.5 m tall; stems glabrous or eglandular-puberulent; lamina 5.5–30 mm long, coriaceous; capsules acute to acuminate, 6–12.5 mm long | macrantha |
| Sprawling to ascending low or mat-forming sub-shrubs to 0.2 m tall; stems eglandular- to glandular-pubescent or rarely glabrous; lamina < 10 mm long, thin or slightly fleshy; capsules emarginate, < 6 mm long | 66 | |
| 66 | Leaves shallowly crenate or toothed; stem hairs patent or antrorse arching, or absent; corolla 5–9 mm diameter | 67 |
| Leaves 3–7-fid; stem hairs stiffly retrorse, straight; corolla (7–)10–20 mm diameter | 68 | |
| 67 | Lax, softly woody sub-shrub; stem hairs antrorse, curved; lamina elliptic to orbicular, shallowly toothed; inflorescence branches hairy | zygantha |
| Compact sub-shrub, cushion or mat plant; stem hairs patent; lamina oblanceolate oblong, elliptic, or rhomboid, shallowly and bluntly toothed or crenate, rarely some leaves entire; inflorescence branches glabrous | planopetiolata | |
| 68 | Leaf margin thickened, minutely papillate; flowers usually solitary, sessile; calyx 5-lobed, hairy to ½-way on outer face | densifolia |
| Leaf margin thin, smooth; flowers 2–3, rarely solitary, distinctly pedicellate; calyx 4-lobed, hairy to apex on outer face | trifida | |
| 69 | Leaves long-petiolate; lamina and calyx with short, curved, eglandular hairs; corolla > 7 mm diameter | 70 |
| Leaves sessile; lamina and calyx with long, straight, eglandular and glandular hairs; corolla < 8 mm diameter | 71 | |
| 70 | Cushion plants with deeply toothed to pinnatifid leaves; flowers solitary or rarely 2–3; calyx lobes pinnatifid or deeply lobed; corolla tube 3.5–7 mm long; seeds weakly flattened, finely papillate, 0.6–1.1 mm long (South Island) | cheesemanii |
| Lax, sprawling or mat-forming plants with crenate leaves; flowers 2–8; calyx lobes usually entire or rarely shallowly toothed; corolla tube 3–4 mm long; seeds flattened, smooth, 1–1.5 mm long (North Island) | spathulata | |
| 71 | Lamina eglandular hairy with a few glandular hairs as well; peduncles 1.5–2 mm long; pedicels 0.3–1.5 mm long; corolla 7–10 mm diameter, lobes 5, sometimes 4; capsules glabrous | birleyi |
| Lamina mixed eglandular- and glandular-hairy; peduncles 5–15 mm long; pedicels 2.5–5 mm long; corolla 18–25 mm diameter, lobes 4; capsules mixed glandular- and eglandular-hairy at apex | spectabilis | |
| 72 | Leaves discolorous: green above and white beneath (sometimes pale buff when dry); pedicel hairs in one row (Fiordland) | catarractae |
| Leaves concolorous or if discolorous pale green beneath or sometimes pinkish; pedicels hairy all around (rarely glabrous) (all New Zealand) | 73 | |
| 73 | Lamina 3–15 × 2–10 mm; width ≥ ⅔ length; margin often crenate or crenate-serrate in 1–4(–10) pairs of teeth or lobes; apex rounded; base truncate or abruptly cuneate | 74 |
| Lamina 5–100 × 1.5–38 mm; width ≤ ½ length; margin often serrate with teeth out-turned at the tip, in 3–15 pairs; apex usually acute to acuminate, sometimes obtuse or rounded; base cuneate | 75 | |
| 74 | Leaves hairy or glabrous; corolla pink or purplish; inflorescences usually glandular-hairy, sometimes eglandular only; seeds 1–3 mm long (North Island) | hookeriana |
| Leaves glabrous; corolla white, rarely bluish or pale pink; inflorescences glabrous or eglandular-hairy, rarely some glandular hairs as well; seeds 0.6–0.8 mm long (South Island) | lyallii | |
| 75 | Stems prostrate to decumbent, purplish-black contrasting strongly with pale green petioles; lamina obovate or oblanceolate (broadest above ½-way) or rarely elliptic; pedicels glabrous or sparsely eglandular or glandular-hairy | melanocaulon |
| Stems usually ascending to sub-erect, or sometimes prostrate or (on cliffs) trailing, reddish or brownish and not contrasting strongly with often reddish petioles; lamina ovate or lanceolate to linear (broadest at or below ½-way) or rarely elliptic; pedicels hairy all around, usually eglandular but sometimes glandular. | 76 | |
| 76 | Calyx lobe outer faces, ovary, capsule, and often leaves hairy with short, straight, pale hairs | senex |
| Ovary, capsule, and leaves glabrous; calyx lobes ciliate and rarely pubescent on outer faces | lanceolata | |
| 77 | Sinus present in vegetative buds at branch tips | 78 |
| Sinus absent in vegetative buds at branch tips | 110 | |
| 78 | Leaves glaucous or glaucescent on one or both surfaces; corolla tube glabrous | 79 |
| Leaves green on both surfaces (although may be dull or glossy on one or both); corolla tube glabrous or hairy inside | 89 | |
| 79 | Leaf bud strongly tetragonous in transverse section (midribs and leaf margins forming defined angles in buds) (North Island) | 80 |
| Leaf bud terete, flattened, or only weakly tetragonous in transverse section (either midribs or margins but not both forming defined angles in buds) (South Island or Three Kings Is.) | 81 | |
| 80 | Corolla tube 3–4.2 mm long, > calyx; margins of calyx lobes eglandular- or mixed glandular- and eglandular-ciliolate; stem with bifarious eglandular hairs; leaves glossy green to dark green above; style 6–9 mm long (west Waikato) | scopulorum |
| Corolla tube 1.8–2.5 mm long, about equal to calyx; margins of calyx lobes glabrous or rarely with a few sparse eglandular cilia; stem glabrous or rarely with sparse bifarious eglandular hairs; leaves dull and glaucous above; style 2.2–4.5 mm long (Kaimanawa Mountains, Kaweka Range, northern Ruahine Range) | colensoi | |
| 81 | Bracts ≥ calyx, surrounding and obscuring calyx in anterior view (east Marlborough) | rupicola |
| Bracts < calyx, not surrounding nor completely obscuring calyx in anterior view (Three Kings Is., west Marlborough, Nelson, Fiordland) | 82 | |
| 82 | Flowers, at least the lowest, on distinct pedicels longer than the bracts (Three Kings Is.) | insularis |
| Flowers, even the lowest, sessile or on short pedicels < bracts (South Island) | 83 | |
| 83 | Inflorescence usually a tripartite compound raceme, sometimes multipartite, rarely a few simple; if simple then lowest bracts without flowers | 84 |
| Inflorescence usually a simple raceme with flowers in even the lowest bracts, rarely a few tripartite | 85 | |
| 84 | Leaves concolorous, dull green to glaucous above and beneath; anterior calyx lobes fused to ⅓-way or more; corolla tube ≤ calyx | dilatata |
| Leaves discolorous, green or yellowish-green above, glaucous beneath; anterior calyx lobes free; corolla tube > calyx | rigidula | |
| 85 | Leaves concolorous, dull and glaucous or glaucescent on both surfaces at least when young | 86 |
| Leaves discolorous, upper surface dull or glossy green but not glaucous | 87 | |
| 86 | Decumbent and sparsely branching shrub; leaf margin glabrous or sparsely ciliate; peduncle 4–7 mm long, < subtending leaf | societatis |
| Suberect to erect shrub; leaf margin glabrous, minutely papillate; peduncle 6–11 mm long, about = the subtending leaf | baylyi | |
| 87 | Leaf midrib finely pubescent above or glabrous (hairs mostly < 0.05 mm long or a few up to 0.075 mm long); leaves 5–22 mm long; lowest flowers usually shortly pedicellate or sometimes sessile (Fiordland, west Otago, south Westland) | cockayneana |
| Leaf midrib coarsely pubescent above (hairs 0.075–0.175 mm long); leaves 6–28 mm long; flowers usually sessile or sometimes shortly pedicellate (Nelson and Marlborough) | 88 | |
| 88 | Leaves entire or shallowly toothed; longest leaves on plant 12–25 mm long; ovules (hermaphrodite flowers) 7–18 | simulans |
| Leaves always entire; longest leaves on plant up to 33 mm long; ovules (hermaphrodite flowers) 15–33 | cryptomorpha | |
| 89 | Leaf undersides with a regular row of short oblique domatia just in from each margin | townsonii |
| Leaves without domatia | 90 | |
| 90 | Leaves glossy above and coriaceous, elliptic to broadly obovate, 45–100 mm long and 21–51 mm wide; apex obtuse, truncate, or slightly retuse; corolla, stamen filaments, and styles dark magenta | speciosa |
| Leaves dull above, or thin, or linear to lanceolate or ovate, or < 25 mm wide, or apex sub-acute to acuminate; corolla white or pale purplish | 91 | |
| 91 | Leaves all or most > 40 mm long, > 4 × as long as broad; inflorescences all or most with > 30 flowers and > 40 mm long; corolla tube hairy inside | 92 |
| Leaves all or most < 40 mm long, < 3.5 × as long as broad; inflorescences all or most with < 30 flowers and mostly < 50 mm long; corolla tube either glabrous or hairy inside | 98 | |
| 92 | Inflorescences usually < the subtending leaves; corolla tube ≤ 2.3 mm long, < calyx; stamen filaments ≤ 3 mm long (Kermadec Is. only) | breviracemosa |
| Inflorescences usually ≥ the subtending leaves; corolla tube > calyx and/or > 2.3 mm long; stamen filaments > 4 mm long (rest of New Zealand) | 93 | |
| 93 | Lateral corolla lobes shorter than corolla tube; leaves linear-lanceolate (North Island south of Hunua Ranges) | corriganii |
| Lateral corolla lobes ≥ the corolla tube; leaves usually linear-lanceolate or broader, rarely linear or linear-lanceolate (Northland or Coromandel and nearby islands, or South Island) | 94 | |
| 94 | Corolla tube > 2 mm wide; lateral corolla lobes broad (about as wide as long) and narrowed abruptly at base (far north of North Island, near Spirits Bay) | adamsii |
| Corolla tube < 2 mm wide; lateral lobes longer than wide and narrowed gradually to base (Coromandel and Hauraki Gulf islands; South Island) | 95 | |
| 95 | Leaf margins entire, pubescent or rarely puberulent; leaves often pubescent beneath, or sometimes glabrous; faces of calyx lobes usually hairy, sometimes glabrous; corolla tube < to about = calyx; tube and lobes often hairy outside, sometimes glabrous; capsules usually hairy at least in septal groove and often all over, sometimes glabrous (Coromandel and Hauraki Gulf islands to Mokohinau Is.) | pubescens |
| Leaf margins entire or with distant minute teeth, puberulent or ciliolate; leaves glabrous beneath; faces of calyx lobes glabrous or rarely hairy towards the base; corolla tube > calyx; tube and lobes glabrous outside (South Island) | 96 | |
| 96 | Leaves either not tapering to a fine point or gradually tapering from about or just past the midpoint; corolla tube often 2 × calyx; ovules 6–12 per locule | leiophylla |
| Leaves tapering to a fine point, often conspicuously narrowed (acuminate) c. ¾ of the way to apex; corolla tube 1–1.5 × calyx; ovules 12–30 per locule | 97 | |
| 97 | Stems usually glabrous, sometimes bifariously or rarely uniformly puberulent; leaves (6–)11–28 mm wide, widest point ½–⅔-way from base; plants of open sites, scrub, and forest margins but rarely swamps or wetlands, throughout South Island. | salicifolia |
| Stems uniformly puberulent; leaves 5.5–11(–14) mm wide, widest point about ⅓-way from base; plants usually in swamps and wetlands, Westland | phormiiphila | |
| 98 | Leaves distinctly shouldered at junction with petiole, to give a broad and shield-shaped sinus; flowers sessile or very shortly stalked, opposite; bracts large and almost leaf-like | 99 |
| Leaves gradually to steeply cuneate to petiole, to give a narrow, acute sinus; flowers mostly pedicellate, usually alternate, or the lower ones opposite; bracts mostly small and very different from leaves (large in V. rupicola, which has a narrow and acute sinus) | 100 | |
| 99 | Midrib beneath keeled throughout; lamina (7–)14–18(–28) mm long, with stomata evident only on the abaxial surface (but on both surfaces at Denniston Plateau and Caswell Sound); margin often minutely crenulate, bevelled; anterior calyx lobes free or fused in lower ⅓; corolla lobes elliptic to broadly elliptic | mooreae |
| Midrib beneath keeled except for short, flattened portion near the apex; lamina 3–9 mm long, with stomata evident on both surfaces; margins smooth, rounded; anterior calyx lobes fused to ⅔ or more; corolla lobes narrowly elliptic to elliptic | pauciramosa | |
| 100 | Leaves with conspicuous, white, dense pubescent margins, contrasting with the glabrous surfaces, plicate-mucronate apex, and petiole; flowers 10–15(–20) mm diameter; calyx > 3.5 mm long | elliptica |
| Leaf margin glabrous or minutely or sparsely hairy without a strong contrast at apex and petiole; flowers usually <10 mm diameter; calyx < 4 mm long | 101 | |
| 101 | Inflorescences simple or sometimes tripartite, with flowers in the axils of lowest bracts | 102 |
| Inflorescences compound racemes, sometimes tripartite or unbranched, but if unbranched then lowest bracts large and not bearing flowers | 108 | |
| 102 | Bracts usually equalling or > calyx, surrounding and obscuring calyx in anterior view; flowers sessile; corolla lobes narrowly acute | rupicola |
| Bracts usually < calyx, not surrounding and obscuring calyx in anterior view; flowers sessile or pedicellate; corolla lobes rounded to obtuse or broadly acute | 103 | |
| 103 | Leaf bud sinus small, rounded, not much longer than broad | leiophylla |
| Leaf bud sinus at least twice as long as broad, narrow and acute | 104 | |
| 104 | Lamina mostly > 20 mm long; anthers white or cream (known from limestone cliffs in a few localities in Fiordland National Park) | arganthera |
| Lamina mostly < 20 mm long; anthers pink to purple (or pale on male-sterile flowers) (mostly Canterbury northwards) | 105 | |
| 105 | Low, openly branching shrubs with spreading branches; internodes usually < 2 × branchlet diameter; leaf apex broad, sub-acute | 106 |
| Bushy, densely branched, rounded shrubs with erect branches; internode usually > 2 × branchlet diameter; leaf narrowing to acute or sometimes sub-acute apex | 107 | |
| 106 | Calyx lobes 1.8–3.1 mm long, obtuse to sub-acute, or rarely acute; corolla tube 1.4–3.5 mm long, usually slightly > calyx; anthers purple; capsule ≤ 2 × calyx | canterburiensis |
| Calyx lobes 1.0–1.5 mm long, usually rounded to obtuse, rarely sub-acute or acute; corolla tube 0.6–1.5 mm long, < calyx; anthers usually pale pink or white; capsule 3–4 × calyx | vernicosa | |
| 107 | Stomata conspicuous on adaxial leaf surface; petiole broadly winged, leaving a narrow sinus in the bud (South Island) | brachysiphon |
| Stomata inconspicuous on adaxial leaf surface; petiole narrowly winged, leaving a broad sinus in the bud (North Island) | venustula | |
| 108 | Low-growing shrub (< 0.5 m tall), often creeping or spreading, sometimes mat-forming; flowers sessile or subsessile; corolla tube about ≤ calyx (South Otago, Southland) | dilatata |
| Erect, bushy shrubs or small trees to 2.5 m or sometimes more; flowers, at least the lowest, distinctly pedicellate; corolla tube ≥ calyx | 109 | |
| 109 | Either some leaves minutely toothed or incised or the anterior calyx lobes fused for most of their length; corolla tube glabrous inside (north of Auckland) | diosmifolia |
| Leaves entire and anterior calyx lobes free for most of their length; corolla tube hairy inside (Nelson, western Marlborough) | subfulvida | |
| 110 | Inflorescence a compound raceme or ternate (Three Kings Is. only) | insularis |
| Inflorescence a simple raceme (North and South Islands) | 111 | |
| 111 | Leaves glaucous, at least beneath, usually glaucous above, but occasionally glaucescent | 112 |
| Leaves green on both surfaces or reddish beneath, often glossy but sometimes dull | 121 | |
| 112 | Flowers, at least the lowest in an inflorescence, borne on obvious pedicels; bracts usually alternate or whorled but sometimes the lowermost opposite | 113 |
| Flowers usually sessile (rarely short pedicels present in V. amplexicaulis and V. buchananii); bracts opposite and decussate, sometimes becoming alternate above | 117 | |
| 113 | Stems and peduncles glabrous; branches often long, trailing, leafless (South Canterbury) | pareora |
| Stems and peduncles minutely hairy or pubescent; branches mostly spreading to erect (Nelson to mid Canterbury or Southland). | 114 | |
| 114 | Stem uniformly puberulent; ovary and capsule minutely hairy; corolla tube < calyx | glaucophylla |
| Stem glabrous or uniformly pubescent, rarely bifariously puberulent to pubescent; ovary and capsule glabrous; corolla tube ≥ calyx | 115 | |
| 115 | Leaves elliptical to rhomboid, tapering to a blunt apex; corolla tube equal or slightly longer than calyx (Southland, Otago) | biggarii |
| Leaves linear-lanceolate to ovate to elliptic or obovate, acute or apiculate at apex; corolla tube usually distinctly > calyx (northern South Island) | 116 | |
| 116 | Dense, neatly rounded shrubs, much branched at tips; leaves 5–23 × 3–8 mm; corolla tube < 2.5 mm long | topiaria |
| Sprawling to erect, usually more open-branched shrubs, with most branches near the base, but sometimes dense, rounded or flat-topped shrubs; leaves 11–42 × 3–17 mm; corolla tube > 2.5 mm long | albicans | |
| 117 | Corolla lobes purplish or bluish when young, sometimes fading to pale pink or white with age | pimeleoides |
| Corolla white, rarely slightly pink in bud and when opening | 118 | |
| 118 | Leaf margins fringed with long hairs, surfaces glabrous except sometimes near the base and midrib above | gibbsii |
| Leaf margins glabrous or ciliolate, or if pubescent then surfaces pubescent also | 119 | |
| 119 | Leaves 2.5–8 × 2–6 mm; leaf bud closely invested with newly separated leaves, hiding the internode below; corolla tube ≤ 2 mm long | buchananii |
| Leaves 7–30 × 4–17 mm; leaf bud separated from newly separated leaves by a short internode; corolla tube ≥ 2 mm long | 120 | |
| 120 | Corolla tube 2–3 mm long | pinguifolia |
| Corolla tube 3.4–4.8 mm long | amplexicaulis | |
| 121 | Most leaves on a plant > 40 mm long, although some may be shorter | 122 |
| Most leaves on a plant < 40 mm long, although some may be longer | 139 | |
| 122 | Leaves cuneately narrowed to branchlet width or less at the base | 123 |
| Leaves wider than branchlet width at the base, usually amplexicaul or rounded at the base | 137 | |
| 123 | Leaves mostly < 5 mm wide, linear; calyx lobes never hairy on faces, although hairy on margins; stamen filaments conspicuously incurved in the bud, straightening as flower opens | 124 |
| Leaves mostly > 8 mm wide or if narrow and linear then the calyx lobes pubescent on faces as well as margins; stamen filaments straight or slightly curved at apex in bud | 125 | |
| 124 | Shrub or small tree; leaf margins usually hairy; leaf surfaces smooth or faintly pitted with small depressions; corolla tube hairy inside | parviflora |
| Shrub; leaf margins usually glabrous; leaf surfaces at least below conspicuously pitted with small depressions, each containing a minute glandular hair with 2 apical cells; corolla tube glabrous inside | stenophylla | |
| 125 | Youngest shoots strongly tinged maroon, purple, or red, or if green, then outsides of leaf buds and undersides of young leaves tinged purple (North Island west coast from Muriwai to Kawhia only; note, some plants similar to V. stricta from Hikurangi Swamp also have this feature) | 126 |
| Youngest shoots green, yellow or orange; outside of leaf buds and undersides of young leaves (apart from margins and midribs) not tinged purple (various North Island localities) | 127 | |
| 126 | Usually prostrate shrub, < 0.5 mm tall; leaves elliptic to obovate, broadest at or above mid-way and obtuse to rounded at apex, 13–55 mm long; margins conspicuously ciliate | obtusata |
| Sprawling to semi-erect shrub, up to 1 m tall; leaves usually lanceolate to narrow-elliptic, broadest below mid-way and acute to acuminate at apex, (20–)40–90 mm long; margins usually minutely ciliolate | bishopiana | |
| 127 | Corolla tube > calyx or rarely (some flowers of V. stricta) about = calyx; corolla lobes oblong, elliptic, or suborbicular, rounded at apex | 128 |
| Corolla tube < or = calyx; corolla lobes ovate to triangular or elliptic, sub-acute to acute at apex | 132 | |
| 128 | Leaves rather soft except in exposed habitats, dull yellowish- to dark green; corolla 3–6(–8.5) mm long (tube + lobe length), 2.5–6.0 mm diameter, corolla tube 1.0–1.5(–1.7) mm wide; stamen filaments 3.0–5.0(–6.5) mm long; capsule 1.3–4.0(–5.2) mm long | 129 |
| Leaves firm, glossy green to dark green; corolla 5–11 mm long (tube + lobe length), 5–9 mm diameter, corolla tube (1.8–)2–3.5 mm wide; stamen filaments 5–12 mm long; capsule 3.8–10 mm long | 131 | |
| 129 | Widest point of leaves ~ ⅛-way from base; leaf base abruptly cuneate | tairawhiti |
| Widest point of leaves ⅓–⅔-way from base; leaf base gradually cuneate | 130 | |
| 130 | Leaves (5.5–)12.0–45.0 mm wide; lamina thin to subcoriaceous; calyx lobes glabrous or hairy on face | stricta |
| Leaves 3–9 mm wide; lamina thin; calyx lobes glabrous on face | angustissima | |
| 131 | Corolla white to purple, sometimes pinkish; calyx lobes obtuse to acute; stamen filaments white to pale purplish; stems pubescent (Northland and Auckland from Ahipara to Kawhia) | macrocarpa |
| Corolla deep red or magenta; calyx lobes rounded to obtuse; stamen filaments magenta to purplish; stems puberulent (Surville Cliffs and surrounding plateau only) | punicea | |
| 132 | Leaves linear-lanceolate to lanceolate or rarely oblanceolate or narrowly elliptic | 133 |
| Leaves oblanceolate to obovate or rarely lanceolate to elliptic | 135 | |
| 133 | Leaves linear to linear-lanceolate, (3–)4–9(–12) mm wide; lamina and midrib green, even at base; plants of river gorges near the water | rivalis |
| Leaves elliptic to oblong-elliptic or oblanceolate, rarely linear-lanceolate; lamina green or yellowish, midrib yellowish, especially at base; plants of scrub and forest margins, slips, outcrops, and coastal sites | 134 | |
| 134 | Large shrub or small tree to 8 m tall; leaves (30–)50–100(–135) × 6–20(–29) mm, often conspicuously narrowed towards apex; calyx lobes hairy outside (upland sites, central and western Northland | flavida |
| Open or spreading shrub to 2.5 m tall; leaves (12–)26–50(–100) × (4.2–)6–10(–20) mm, often more evenly tapered towards apex; calyx lobes often glabrous outside, sometimes hairy (mostly coastal and lowland sites, eastern Northland and North Cape to Cape Reinga) | ligustrifolia | |
| 135 | Calyx lobes red; calyx margin very densely glandular-ciliolate with a few eglandular hairs; corolla lobes purplish, pink, red, or carmine, fading whitish; capsule 7–8 × 5–6 mm; seeds 1.8–2 mm long | perbella |
| Calyx lobes green sometimes with pink margins; calyx margin mixed eglandular- and glandular-ciliolate, 0.075 mm long; corolla lobes flushed pale purple, fading white; capsule < 5.5 × 4.0 mm; seeds 1–1.8 mm long | 136 | |
| 136 | Stems uniformly puberulent; lamina oblanceolate to obovate; corolla tube 3–5 mm long, puberulent inside, lobes pale mauve | bollonsii |
| Stems glabrous or rarely bifarious puberulent; lamina lanceolate, elliptic, or oblanceolate; corolla tube 1–1.5 mm long, glabrous inside, lobes white | saxicola | |
| 137 | Leaf at least 8 times as long as broad, broadest at the base and tapering evenly to narrow apex; midrib above often yellowish at base (Gisborne and northern Hawke’s Bay) | tairawhiti |
| Leaf 4–6 times as long as broad, broadest between lower third and halfway; midrib green throughout (Chatham Is.) | 138 | |
| 138 | Tree when mature; pedicel pubescent; corolla tube ≤ 2 mm long, < calyx, < corolla lobes | barkeri |
| Shrub; pedicel puberulent; corolla tube ≥ 2.5 mm long, ≥ calyx, > or about = corolla lobes | dieffenbachii | |
| 139 | Inflorescence a compound raceme, rarely ternate; seeds papillate (Three Kings Is.) | insularis |
| Inflorescence a simple raceme; seeds smooth (throughout New Zealand) | 140 | |
| 140 | Leaves linear to narrow oblong, usually > 3 × as long as wide, usually rather dull yellowish-green | 141 |
| Leaves narrowly to broadly elliptical or ovate, usually < 3 × as long as broad, glossy light to dark green or bronze-green at least adaxially | 147 | |
| 141 | Corolla tube distinctly > calyx | 142 |
| Corolla tube ≤ calyx | 145 | |
| 142 | Leaves linear to linear-lanceolate, rather thin, tapering gradually from halfway to a narrowly acute apex; corolla lobes oblong, erect or sub-erect, their width ≤ the width of the corolla tube | angustissima |
| Leaves linear or linear-oblong, subcoriaceous, tapering rather abruptly to an acute apex; corolla lobes ovate to suborbicular, erecto-patent to recurved, their width > the width of the corolla tube | 143 | |
| 143 | Corolla tube about 3 × as long as calyx and hairy inside; capsules 3–4 × calyx | traversii |
| Corolla tube either ≤ 2 × calyx or, if longer then glabrous inside; capsules about 2 × calyx | 144 | |
| 144 | Shrub or small tree; leaf margins usually hairy; leaf surfaces smooth or faintly pitted with small depressions; corolla tube hairy inside | parviflora |
| Shrub; leaf margins usually glabrous; leaf surfaces at least below conspicuously pitted with small depressions, each containing a minute glandular hair with 2 apical cells; corolla tube glabrous inside | stenophylla | |
| 145 | Vegetative bud flattened in cross-section; leaves often yellow on midrib especially near base; calyx lobes acute to acuminate, 1.7–3 mm long; corolla lobes acute, pale purple when young (Northland) | ligustrifolia |
| Bud rounded in TS; leaf midrib green; calyx lobes rounded to acute at apex, 1.2–1.7 mm long; corolla lobes rounded, white (South Island) | 146 | |
| 146 | Leaf adaxial surface glossy; corolla tube 0.7–1.2 mm long; style glabrous, but ovary and capsule hairy (on marble in north-west Nelson) | calcicola |
| Leaf adaxial surface dull; corolla tube 1.4–2.9 mm long; style, ovary, and capsule either all hairy or all glabrous (Banks Peninsula) | strictissima | |
| 147 | Low-growing coastal plants of Chatham Is.; leaves dull green; calyx lobes narrowly deltoid, acute to acuminate, tapering evenly from base | chathamica |
| Low-growing to erect plants of North Island or South Island; leaves dull or glossy green; calyx lobes ovate to elliptic, obtuse to acute, tapering from about mid-way | 148 | |
| 148 | Ovary and capsule hairy | 149 |
| Ovary and capsule glabrous | 150 | |
| 149 | Leaves mostly 6–20 mm (rarely to 30 mm) long; corolla lobes ciliolate on margins | rakaiensis |
| Leaves mostly 20–45 mm (rarely some leaves 13–20 mm) long; corolla lobes glabrous on margins | calcicola | |
| 150 | Sprawling, low-growing (rarely erect) shrubs; leaves elliptic to obovate, glossy bronze or dark green above; leaf margin usually red, ciliate or ciliolate or rarely glabrous | 151 |
| Erect, bushy shrubs; leaves lanceolate to ovate, glossy or dull bright green; leaf margin green, glabrous or minutely puberulent | 152 | |
| 151 | Leaves 6.5–23.5 × 2–13 mm, glossy yellowish or bronze green above and beneath, surfaces glabrous, margin glabrous or with short, tapering, stiff hairs; inflorescence 6–30 mm long with 2–25 flowers; pedicels 0.2–1.7 mm long, mixed glandular- and eglandular-hairy; calyx lobes 1–1.5 mm long; corolla tube 3–6 mm long, >> calyx, glabrous inside. | decumbens |
| Leaves 13–55 × 7.0–28.5 mm, glossy green to dark green above, dull pale green beneath, surfaces usually hairy along midrib and sometimes on surface beneath, margin ciliate with long, soft hairs; inflorescence 38–126 mm long with 34–88 flowers; pedicels1.0–3.3 mm long, eglandular-hairy; calyx lobes 1.5–2.2 mm long; corolla tube 2.3–4.0 mm long ≥ calyx, eglandular-hairy inside | obtusata | |
| 152 | Leaves lanceolate to elliptic, usually very glossy green; margin glabrous (although sometimes minutely papillate in V. urvilleana), usually with narrow translucent border (South Island) | 153 |
| Leaves elliptic to obovate, not very glossy; margin minutely puberulent (North Island) | 155 | |
| 153 | Corolla 4–6 mm diameter, lobes 2–3 mm long (lowland D’Urville I. and the Bryant Range, Nelson) | urvilleana |
| Corolla 5–10 mm diameter, lobes 3–6 mm long (subalpine to alpine South Island) | 154 | |
| 154 | Leaves more or less flat, lanceolate, elliptic or oblong-elliptic, rarely linear-lanceolate; apex subacute to acute, not or only very weakly plicate-acuminate; corolla tube 1–2.2 mm long, eglandular-hairy inside; seeds 1.2–2 mm long. | subalpina |
| Leaves weakly dished, elliptic to obovate, sometimes oblanceolate; apex obtuse to rounded and minutely plicate-acuminate; corolla tube 1.9–3.5 mm long, eglandular-hairy, glandular-hairy or glabrous inside; seeds 0.9–1.5 mm long. | treadwellii | |
| 155 | Leaves elliptic, obovate to oblanceolate, usually obtuse, mostly < 20 mm (rarely to 28 mm) long; stomata evident and crowded on abaxial surface; inflorescence 14–50 mm long, with 15–40 flowers (Tararua Range) | evenosa |
| Leaves linear-lanceolate to narrow-elliptic, mostly > 20 mm long (sometimes 13–20 mm); stomata not evident on abaxial surface; inflorescence 30–90 mm long, with 28–68 flowers (Ruahine Range) | truncatula |
About 450 spp., worldwide but mostly temperate and often alpine, with most diversity in Eurasia and New Zealand. One hundred and twenty-two species indigenous; 118 of these endemic to New Zealand; 19 species naturalised.
Number of species and named hybrids in New Zealand.
| Category | Number |
|---|---|
| Indigenous (Endemic) | 118 |
| Indigenous (Non-endemic) | 4 |
| Exotic: Fully Naturalised | 16 |
| Exotic: Casual | 1 |
| Origin uncertain: Present in wild | 2 |
| Total | 141 |
Wild hybrids between indigenous species of Veronica occur occasionally and a few are quite common, such as V. ×lewisii and the hybrids between V. odora and several whipcord hebes. In addition the genus has a reputation for extensive hybridisation in cultivation, where over 1000 cultivars, many of hybrid origin, have been given cultivar names under the International Code of Nomenclature of Cultivated Plants (see Metcalf 2006 for a comprehensive treatment of cultivars). The following wild and cultivated hybrids have been given hybrid binomial names under the International Code of Nomenclature for Algae, Fungi, and Plants (Turland et al. 2018). See Garnock-Jones (2008) for more detail on nomenclature and hybrid origins. Additional wild hybrids have been reported but not given scientific names.
Veronica ×affinis (Cheeseman) Garn.-Jones, New Zealand Journal of Botany 46: 524 (2008).
Hybrid parentage: Wild origin, Veronica macrocarpa × V. stricta var. stricta (Cheeseman 1925, Cockayne & Allan 1926).
Veronica ×andersonii Lindley & Paxton, Paxton’s Flower Garden 2: t. 38 (1851, as V. andersonii).
Hybrid parentage: Garden origin, thought to be V. stricta var. stricta × speciosa (Cockayne & Allan 1926, Heenan 1994).
Veronica ×balfouriana Hook.f., Botanical Magazine 123: t. 7556 (1897, as V. balfouriana).
Hybrid parentage: Garden origin, thought to be V. pimeleoides × vernicosa (Moore in Allan 1961)
Veronica ×bidwillii Hook., Icones Plantarum, t. 814 (1864, as V. bidwillii).
Hybrid origin: Wild origin, V. decora × lyallii (Ashwin in Allan 1961, Garnock-Jones & Lloyd 2004).
Veronica ×carsei Petrie, Transactions of the New Zealand Institute 55: 96 (1924, as V. carsei).
Hybrid origin: Wild origin, V. stricta var. stricta × venustula (Cockayne & Allan 1926, Bayly & Kellow 2006).
Veronica ×cassinioides Petrie, Transactions of the New Zealand Institute 47: 52 (1915, as V. cassinioides).
Hybrid origin: Wild origin, V. odora × either V. hectorii or V. annulata (Bayly & Kellow 2006).
Veronica ×divergens Cheeseman, Manual of the New Zealand Flora: 502 (1906, as V. divergens).
Hybrid origin: Wild origin, thought to be V. elliptica × leiophylla (Moore in Allan 1961).
Veronica ×edinensis R.Linds., Gardeners’ Chronicle 48: 103 (1910).
Hybrid origin: Garden origin, described as V. hectorii × V. pimeleoides.
Veronica ×erecta Kirk, Transactions of the New Zealand Institute 28: 517 (1896, as V. erecta).
Hybrid origin: Garden origin, thought to be V. pimeleoides × salicifolia (Moore in Allan 1961).
Veronica ×fairfieldii Hook.f., Botanical Magazine 49: t. 7323 (1893). ≡ Veronica hulkeana var. fairfieldii (Hook.f.) Kirk, Transactions of the New Zealand Institute 28: 518 (1896).
Hybrid origin: Garden origin, V. hulkeana × lavaudiana.
Veronica ×franciscana Eastw., Leaflets of Western Botany 3: 221 (1943, as V. franciscana).
Hybrid origin: Garden origin, V. elliptica × speciosa (Heenan 1994).
Veronica ×kirkii J.B.Armstr., New Zealand Country Journal 3: 58 (1879, as V. kirkii).
Hybrid origin: Wild origin, thought to be V. salicifolia × perhaps V. rakaiensis (Moore in Allan 1961).
Veronica ×laevastonii (Cockayne & Allan) Garn.- Jones, New Zealand Journal of Botany 46: 525 (2008).
Hybrid origin: wild origin, V. venustula × V. tetragona subsp. subsimilis (Bayly & Kellow 2006).
Veronica ×leiosala (Cockayne & Allan) Garn.- Jones, New Zealand Journal of Botany 46: 526 (2008).
Hybrid origin: Wild origin, described as leiophylla × salicifolia (Cockayne & Allan 1926).
Veronica ×lewisii J.B.Armstr., Transactions of the New Zealand Institute 13: 357 (1881, as V. lewisii).
Hybrid origin: Wild origin, V. elliptica × salicifolia (Moore in Allan 1961, Metcalf 2001, 2006).
Veronica ×loganioides J.B.Armstr., New Zealand Country Journal 3: 59 (1879, as V. loganioides).
Hybrid origin: Wild origin, perhaps V. odora or V. macrantha × a whipcord hebe (Moore in Allan 1961, Garnock-Jones 2008).
Veronica ×simmonsii Cockayne, Transactions of the New Zealand Institute 48: 202 (1916).
Hybrid origin: Wild origin, V. stenophylla × V. stricta var. stricta.
Veronica ×uniflora Kirk, Transactions of the New Zealand Institute 28: 522 (1896, as V. uniflora).
Hybrid origin: Wild origin, V. densifolia × V. thomsonii (Mark & Adams 1973; H. M. Meudt in Garnock-Jones 2008).
Veronica ×wallii Garn.-Jones, New Zealand Journal of Botany 46: 527 (2008).
Hybrid origin: Garden origin, parentage unknown.
n = 6–63 (Albach et al. 2008, Hair 1967, 1970).
Treatment of the indigenous species closely follows Bayly & Kellow (2006; hebes and semi-whipcord hebes), Meudt (2008, snow hebes), Garnock-Jones (1993; sun hebes), and Garnock-Jones & Lloyd (2004, speedwell hebes and similar plants). Treatment of naturalised species follows Flora Europaea (Walters & Webb in Tutin et al. 1972) and Albach et al. (2004).
Cultivated species and cultivars
In addition to the species treated here, V. longifolia and V. umbrosa are commonly cultivated in New Zealand; the latter is distinguished from the similar V. chamaedrys under that species. Other species are occasionally found in cultivation, including V. perfoliata, V. derwentiana, and V. nivea.
A very large number of cultivars in Veronica sect. Hebe have been selected and named in New Zealand and overseas (mostly as Hebe). Many of these are spontaneous garden hybrids of undocumented parentage, but a few are minor variants of known species (e.g., flower colour variants or variegated forms). It is not possible in a treatment of this kind to mention and describe them all; the most comprehensive treatment is by Metcalf (2001, 2006, as Hebe). A few are mentioned here under the species treatments.